[논문 리뷰] Intra- and Inter-Modal Curriculum for Multimodal Learning
https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3581783.3612468
Intra- and Inter-Modal Curriculum for Multimodal Learning | Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia
Publication History Published: 27 October 2023
dl.acm.org
수식이 많은 논문이라 모든 내용을 리뷰하기엔
티스토리의 수식 입력 시스템상(latex 코드 수동 입력) 한계가 많아서 아이디어 위주로만 정리!
Abstract
멀티 모달 러닝이 주목받고 있지만, 특정 모달리티가 지배적인 상황에서는 modal encoder의 최적화가 덜 된다는 것이 확인되었다.
기존의 방식은 두 가지 문제점이 있다.
1. inter-modal 균형에만 초점을 둬서 각 모달리티 별 intra-modal 데이터의 영향을 고려하지 않는다.
2. 개별 성능에만 치중해서 modal interaction(e.g., visual question answering) task에 부적합하다.
이 문제를 해결하기 위해, 이 논문은 Intra- and Inter-Modal Curriculum Learning framework(I^2MCL) 모델을 제안한다. 이는 데이터 difficulty와 modality balance를 동시에 고려한다.
Intra-modal curriculum에서는 difficulty 측정자로 knowledge distillation loss를 얻기 위해서 사전 학습 teacher 모델을 사용한다.
Inter-modal curriculum에서는 Pareto 최적화를 사용하여 distillation loss 와 task loss로부터 나온 gradients를 측정 및 비교하여 모달리티가 teacher로부터 task를 배울 수 있도록 한다.
이 모델은 under-optimized modality problem을 해결할 수 있다.
1. INTRODUCTION
- Since numerous tasks in the real world involve multiple modalities, multimodal learning has become increasingly important.
- modal fusion problem: 모달리티를 합치면 모달 각각의 성능이 오른다.
- modal interaction problem: 모달리티 사이의 상호관계를 필요, query or retrieve로 합쳐져 예측하는 것,
그러나, modal encoder와 representaions가 단일 모달리티 모델보다 덜 최적화 된다는 것이 발견되었다. Figure 1.이 증거.
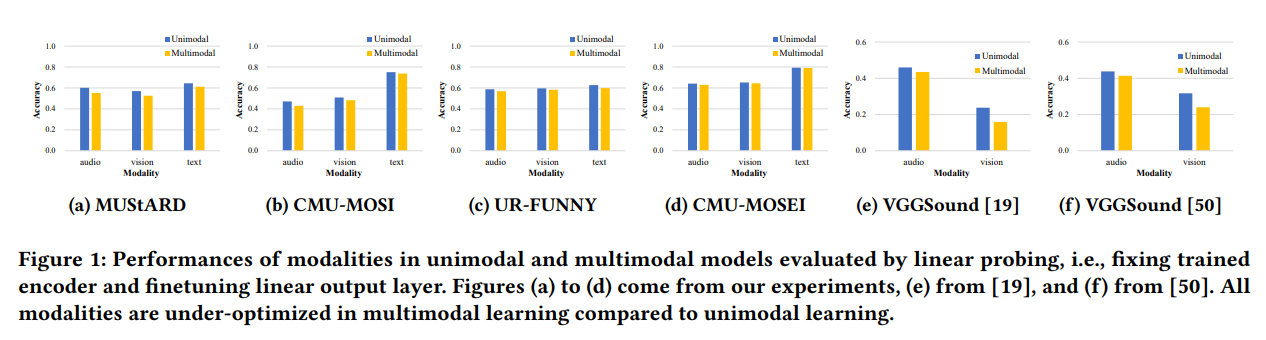
이전 연구에서 이 문제를 여러번 다뤘지만, 그 정의와 원인에 대한 충분한 동의를 얻지 못했다. 예를 들면, 이 문제는 “modality failure” in [19], “greedy nature” in [73] and “modality collapse” in [34]로 불리고, “suppression of dominant modalities” in [50] and “different convergence rates” in [67, 70]로 인해 생겨난다고 주장했다.
주장들을 요약해보면 아래와 같다.
1. 모달리티 별로 최적화 방식이 달라서, 한 가지 전략은 불충분하다.
2. 지배적인 모달리티에 의해 약한 것이 충분히 학습되지 못한다.
따라서, 모달리티 사이의 balance를 개선하면 이 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
이 balance를 개선하기 위해 제안된 방법들도 두 가지 문제가 있다.
1. inter-modal imbalance 문제만 고려한다. intra-modal 데이터의 영향은 고려하지 않는다. 예를 들면, 모달 인코더가 어렵거나 노이지한 데이터만 연속적으로 받았을 때, representation은 결국 잘못된 결과를 도출한다.
2. 강한 모달리티를 억제하려고 하지, 약한 모달리티가 강한 모달리티에 주는 영향은 고려하지 않는다.
(이에 대한 고찰은 3.2에서 다룸.)
따라서, intra-modal 데이터의 관점에서 생각해 강약에 상관 없이 모든 모달리티 성능을 개선해야한다.
어떻게 data difficulty and modality imbalance를 측정하는지는 여전한 어려움으로 남아있다. 최근 modality imbalance를 다루는 metrics들은 modal fusion tasks 에 적합하고 modal interaction problem에는 적합하지 않다.
이러한 문제들을 다루기 위해, 이 논문은 Intra- and Inter-Modal Curriculum Learning framework (I^2MCL)을 제안한다.
Intra-modal curriculum에서는 data difficulty 측정자로 사용되는 knowledge distillation loss를 얻기 위해서 사전 학습 teacher 모델을 사용한다. 이는 모달리티 안에서 data weights를 측정하여 모든 모달리티가 easy-to-hard 방식으로 최적화 되게 한다.
Inter-modal curriculum에서는 Pareto 최적화를 사용하여 각각의 모달 인코더로부터 backpropagated된 distillation loss and task loss 사이의 gradient 관계를 측정한다. 이는 모달리티 사이를 비교하여 어떤 모달리티가 teacher로부터 이 task를 배워야 하는지를 결정한다.
• We present a new perspective from intra-modal data and intermodal mutual influence to explain the under-optimized modality problem in multimodal learning.
• We propose an intra- and inter-modal curriculum framework to address the problem by considering data difficulty and modality balance, applicable to both modal fusion and interaction tasks.
• Empirical experiments demonstrate the benefit and improvement our method brings compared to existing works.



